Introduction: Prof. Chen Xueyuan from the Institute of Physical Education of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and Prof. Liu Ruzhen from the Department of Chemistry of the Taiwan University and the research team led by Dr. Lin Qunzhe, for the first time, successfully prepared Mn4+-doped K2TiF6, K2SiF6, NaYF4 and NaGdF4 red phosphors using high-efficiency ion exchange methods. It has higher lumen efficiency than nitride red phosphor.
White LEDs have become the next generation of lighting due to their energy saving, environmental protection and long life. At present, commercial white LEDs mainly use blue light wafer to excite YAG:Ce3+ yellow phosphor, and the blue light emitted by the wafer is mixed with the yellow light emitted by the phosphor to form white light. . However, the red light component of the emission spectrum of YAG:Ce3+ phosphor is insufficient, resulting in the use of a single YAG:Ce3+ phosphor, which cannot obtain a low correlated color temperature (CCT<4500 cri="">80), so it is limited to indoor general purpose. In the lighting.
In order to solve this problem, a suitable red phosphor is added to the component to supplement the red component, thereby preparing a warm white LED with low color temperature and high color rendering index. At present, commercial red light phosphors with good performance are mainly rare earth doped nitrogen (oxygen) materials, but such phosphors have limitations such as excessive emission bandwidth and high pressure for preparation, resulting in low lumen efficiency and price. expensive. Therefore, the development of low-cost, narrow-band emission red phosphors that can be effectively excited by blue-light wafers, especially the replacement of rare-earth luminescent materials, has become the focus of attention, which is also the key to improving the lumen efficiency of warm white LEDs.
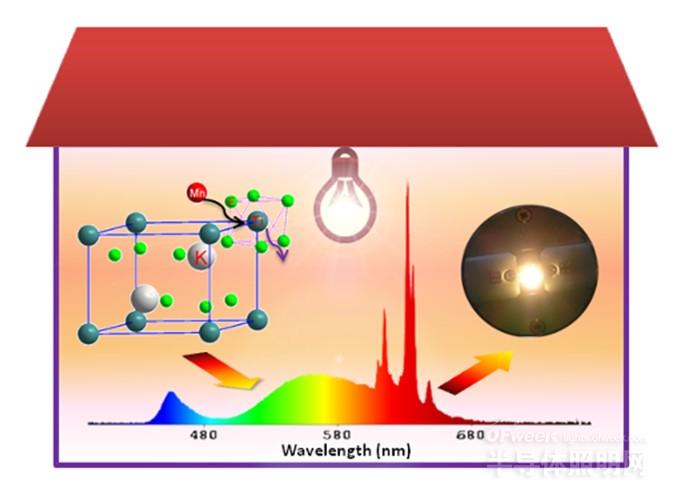
K2TiF4:Mn4+ red phosphor synthesized by wet chemical method and high-efficiency warm white light emitting diode
Professor Chen Xueyuan from the Fujian Institute of Physical Education of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and Professor Liu Ruqi from the Department of Chemistry of the Taiwan University and the research team led by Dr. Lin Qunzhe successfully prepared Mn4+-doped K2TiF6, K2SiF6, NaYF4 and NaGdF4 red phosphors for the first time using high-efficiency ion exchange methods. The phosphor has a strong absorption band (bandwidth ~50 nm) at ~460 nm, which is very suitable for the excitation of blue light wafers, and its emission is a sharp line red light emission of ~630 nm, compared with nitrogen (oxygen) red light fluorescence. Powder has a higher lumen efficiency.
K2TiF6: Mn4+ phosphor has an absolute quantum efficiency of 98% at room temperature, which is superior to most existing red phosphors. At the same time, the phosphor has good fluorescence thermal stability, and its luminescence intensity at 150 degrees reaches room temperature. 98% below. The warm white LED packaged by the combination of the red phosphor and the YAG:Ce3+ yellow phosphor has a lumen efficiency of 116 lm/W at a driving current of 60 mA, a color temperature of 3556 K, and a color rendering index (Ra) of 81. The ion exchange preparation method developed by the research team is simple, can be prepared at room temperature and normal pressure, and the raw material price is cheap, so it has a good market application prospect.
In addition, the research team also conducted an in-depth study on the spectral properties of Mn4+ ions in fluoride matrix. The low-temperature high-resolution laser spectroscopy revealed its electronic energy level structure and explained its abnormal luminescence intensity-temperature dependence. These provide a reliable theoretical basis for further research and development of such non-rare earth red light-emitting materials. The above research results were published in full text on July 8, 2014 in Nature-Communication (Nature. Commun. 2014, DOI: 10.1038/ncomms5312).
In recent years, the research team led by Professor Liu Ruzhen has studied the basic and practical applications of inorganic luminescent materials, except for internationally important journals such as Angew. Chem. It. Edit., J. Am. Chem. Soc., Chem. Mater. In addition to publishing a number of important works (four of which were published by ESI as highly cited papers), more than 60 patents have been obtained.
This kind is wet and dry Vacuum Cleaner. Just as its name implies,it can use not only in wet place,but also in dry place. Its function will be power. In this style,there is a vacuum cleaner that is very special,it has crevice nozzle,so it can cleanr more thoroughly. Hope you will like it,now let's see some pictures blow.




Wet&Dry Vacuum Cleaner, Industrial Wet And Dry Vacuum Cleaner, Wet Dry Vacuum Cleaner
Ningbo ChinaClean Household Appliances Manufacture Co., Ltd. , https://www.chinaclean-elec.com
