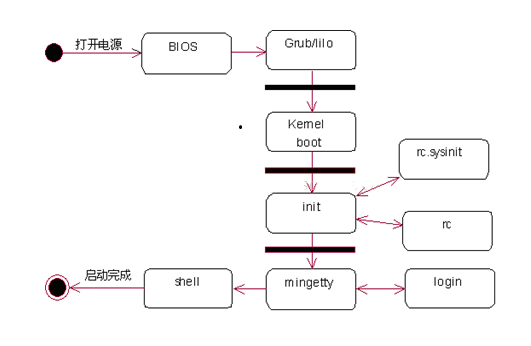
Kernel boot phase
1, bootsect phase
2, setup stage
3, head.S stage
4, main.c stage
Init phase (1)
1. Determine user login mode
The following login modes are listed in "/etc/inittab", including single-person maintenance mode, multi-user non-network mode, text interface multi-user mode, and X-Windows multi-user mode. One-person maintenance mode (runlevel is 1) is similar to the "security mode" in Windows. In this case, the system does not load a complex mode so that the system can start normally. The most common of these modes is 3 or 5, where the default in this system is 5, which is the X-Windows multi-user mode.
#Default runlevel. Therunlevels usedby RHS are:
# 0 - halt (Do NOT set initdefault to this)
# 1 - Single user mode
# 2 - Multiuser, without NFS (The same as 3, if you do not have networking)
# 3 - Full multiuser mode (text interface startup mode)
# 4 - unused
# 5 - X11 (Graphics Startup Mode)
# 6 - reboot (Do NOT set initdefault to this)
#
Id:5:initdefault:
Init phase (2)
2. Execute the script /etc/rc.d/rc.sysinit
After confirming the login mode, it is necessary to start reading Linux host information into the Linux system. The content is in the file "/etc/rc.d/rc.sysinit". Looking at this file, it can be seen that the default path, host name, network information recorded in "/etc/sysconfig/network", etc. are determined here.
#System initialization.
Si::sysinit:/etc/rc.d/rc.sysinit
Init phase (3)
3. Start the kernel plug-in module and each run-level script
Here, it is mainly to read the module load configuration file (/etc/modules.conf) to confirm which modules need to be loaded. Next, according to different runlevels, run the "/etc/rc.d/rc" script with parameters (runlevels) to load different modules and start system services. The init process waits for the return of the "/etc/rc.d/rc" script.
L0:0:wait:/etc/rc.d/rc 0
L1:1:wait:/etc/rc.d/rc 1
L2:2:wait:/etc/rc.d/rc 2
L3:3:wait:/etc/rc.d/rc 3
L4:4:wait:/etc/rc.d/rc 4
L5:5:wait:/etc/rc.d/rc 5
L6:6:wait:/etc/rc.d/rc 6
Init phase (4)
4. Enter the user login interface
The system also needs to configure some abnormal shutdown processing. Finally, several virtual terminals (tty1~tty6) are opened by "/sbin/mingetty" for user login. If the run level is 5 (the graphical interface is started), the xdm program is run to provide the user with the login mode of the xdm graphical interface. If you open a virtual terminal locally, when the terminal times out and no one logs in or no one presses the key for a long time, the terminal will exit the execution. The "respawn" in the script tells the init process to re-open the terminal. Otherwise, after a while, After that, we will find that the terminal has disappeared and cannot be switched using ALT+Fn.
Init phase (5)
#Trap CTRL-ALT-DELETE
Ca::ctrlaltdel:/sbin/shutdown-t3 -r now
#When our UPS tells us power has failed, as we have a few minutes
Pf::powerfail:/sbin/shutdown-f -h +2 "Power Failure; System Shutting Down"
#If power was restored before the shutdown kicked in, cancel it.
Pr:12345:powerokwait:/sbin/shutdown-c "Power Restored; Shutdown Cancelled"
#Run gettysin standard runlevels
1:2345: respawn:/sbin/mingettytty1
2:2345: respawn:/sbin/mingettytty2
3:2345: respawn:/sbin/mingettytty3
4:2345: respawn:/sbin/mingettytty4
5:2345: respawn:/sbin/mingettytty5
6:2345: respawn:/sbin/mingettytty6
#Run xdmin runlevel5
x:5:respawn:/etc/X11/prefdm-nodaemon
The program flow is as follows:
Storage Inverter,Energy Storage Inverter,Bi Directional Inverter,PV Bi Directional Inverter
Jinan Xinyuhua Energy Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.xyhenergy.com
