The cost of the power battery is close to 50% of the total cost of the vehicle. With the subsidy falling, the lithium battery industry is bound to face a price reduction test. However, how to reduce the cost of power batteries becomes a problem that the industry must face in the post-subsidy era when the current high quality production capacity is still insufficient.
Background: Lithium ore prices remain the same
The most difficult part of the cost reduction of power batteries comes from the price pressure of upstream materials, among which the price of lithium ore from the positive materials of the four major materials has the most significant impact.
Since 2015, with the initial outbreak of the new energy automobile market in China, the demand for power batteries has skyrocketed, and the cathode material price has become the most significant. The giants who have mastered a large amount of lithium mineral resources in the upper reaches have controlled the price of cathode materials.
As early as the end of last year, Australian lithium giant Galaxy announced the signing of a five-year binding underwriting agreement with several customers in Asia, and sold 200,000 tons of lithium concentrate annually. In the meantime, the planned production of the Mt Cattlin mine will be sold. Alas, the overall price level in 2018 is higher than that in 2017.
China's salt lake is low in lithium, and lithium is heavily dependent on imports
The direct impact of this was the price increase of lithium carbonate. On February 23, Sichuan battery grade lithium carbonate prices rose by 5,000 to 165,000 yuan per ton, or 3.13%; Jiangsu battery grade lithium carbonate rose by 10,000 yuan to 170000 yuan / ton, or 6.25%; Lithium hydroxide rose 3,000 yuan to 153,000 yuan / ton, or 2%. The overall rise in the price of lithium salt, on the one hand may be due to subsidy policy landing, while new energy vehicles and power batteries into the consumer season, on the other hand may reflect the slow release of lithium ore and lithium salt supply capacity.
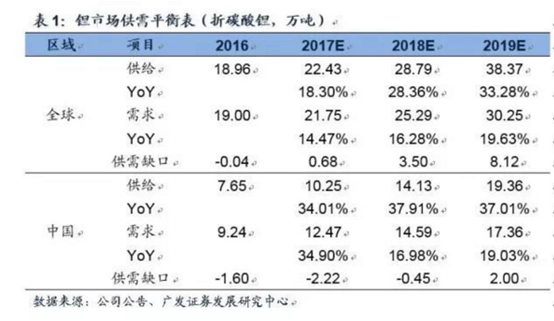
China's salt lake is inherently deficient (high magnesium-lithium ratio and low lithium concentration). At present, the production capacity is mainly industrial grade, and it is difficult to impact the battery-level market in the short term. Domestic salt lakes are mostly located in areas with harsh natural conditions. Affected by weather, energy, and transportation, the actual output of salt lakes is highly uncertain. At the same time, the release of new production capacity is also subject to uncertainties in factors such as process technology, product quality, and reliability and stability. At present, China accounts for about 10% of the lithium output from the global salt lake. It is expected that this proportion will remain low for a long time. Recently, a number of companies have successively announced that lithium carbonate has been successfully extracted from salt lakes. However, most of them are experimental projects and do not have the capability of large-scale production. The visual impact is far beyond the actual disturbance to the supply side.
Is there any basis for the price reduction of the four core materials?
In this situation, does the four materials have room for price reduction?
At present, among the four key materials, the proportions of the positive electrode, negative electrode, separator, and electrolyte in the power battery cost are about 40%, 20%, 8%, and 10%, respectively, which together account for nearly 80% of the cost. Whether it can reduce the cost of these four key materials is significant for power batteries.
In addition to being limited to the lithium production capacity of the basic raw materials, cathode materials are more affected by cobalt materials. As the domestic material route gradually shifts from lithium iron phosphate to ternary, demand for cobalt materials soars. In terms of cobalt prices, cobalt mines are highly dependent on imports, and the demand for cobalt from lithium batteries continues to grow. It is expected that the cobalt price will continue to rise in 2018.
From this point of view, the high prices of raw materials lithium and cobalt will form a support for the price of cathode materials this year, and the ternary materials will continue to rise as a high probability event.
Does this mean that the cathode material cannot be reduced this year? The answer is that the pressure to control costs has shifted from lithium giants to cathode materials companies.
At present, there are three ways to reduce costs in the industry: First, the cathode material company does not allow profit. The performance of lithium iron phosphate was significant last year. The gross profit margin of a large-scale enterprise dropped from 43.67% in 2016 to 32.5%, down 11.17%. Under the pressure of downstream price cuts and increased competition this year, further profitability is possible.
The second is to control the upstream raw materials. The power battery company manages the cost of cathode materials by laying out lithium resources and cobalt resources, as well as recycling layouts, and building or finding external products for lithium salt and cobalt intermediate products.
The third is "decrease cobalt" or even "cobalt." High nickel ternary (referring to NCM622, 811) is the most feasible method, and there are even trends in skipping NCM622 direct 811 within the industry. According to calculations, after adopting 811, the overall unit cost has dropped by 7%. At the same time, research on new cathode materials such as lithium nickel manganese oxide, lithium nickelate, lithium manganese phosphate, and lithium-rich manganese base has made good progress.
In terms of anode materials, 2017 was affected by the rising prices of needle coke in raw materials, and artificial graphite experienced several price increases to break the calm in recent years. In order to control costs, many negative companies in the top ten abandoned their outsourcing OEMs and increased their own graphitization production capacity. In 2018, the supply of raw materials, petroleum coke and needle coke, eased and the prices tended to stabilize.
As the new graphitization capacity starts to be released from May to June this year, the price of anode materials may gradually decline. After searching for anode materials, the company found that the high-end graphite cathode can withstand a price reduction of up to 20%, and the overall affordable price reduction is about 10%.
On the diaphragm side, production capacity will be further released and price reductions are possible. A large amount of capital investment and new production capacity in this area has prompted the industry to raise price wars. In the year 2018, large diaphragm companies announced that they would actively reduce their prices by 20%. According to a survey conducted by a research organization, this year's large-scale top separator companies are still increasing their production capacity. The release of new production capacity will cause the diaphragm to face a price drop of more than 20% in 2018.
It is worth mentioning that, on the basis of the improvement of dry diaphragm technology and the ability to meet the performance requirements of power batteries, the tendency of power battery companies to switch from the use of dry diaphragms to wet diaphragms is becoming more apparent.
According to the relevant data, the difference between domestic dry and wet membrane prices is about 1-1.5 yuan per square meter. With 1GWh battery capacity, the required amount of diaphragm (without loss) is 1550-18.50 million square meters, the processing and coating price is about 1 yuan/per square meter, and 1GWh of power battery is made with a dry diaphragm, which can save at least the wet diaphragm. With a cost of 15.5 million yuan, the cost of the diaphragm can be reduced by about 40% for large power battery manufacturers.
With regard to electrolytes, the price war continues and there is limited space for price cuts. Last year, mainly due to the rapid rise of some battery companies, the rapid expansion of demand at the same time, the bargaining price is also very powerful. Some electrolyte companies in order to seize the market share, rather than sacrifice profits to achieve, causing the electrolyte price competition is fierce.
With the increase in the supply of raw materials of lithium hexafluorophosphate this year, the price may be reduced, but the rate is slowing down; the price of solvents fluctuates, but the cost has little effect. Overall, the electrolyte industry is relatively transparent in price, and there is not much room for decline in conjunction with power batteries. The decline is expected to be only about 5%.
Raising the yield rate is the key to controlling costs
If the material is subject to fluctuations due to the influence of supply and demand, increasing the yield of the battery manufacturing process is the key to reducing the cost of the power battery from the downstream.
In fact, the level of manufacturing capacity is mainly reflected in the yield rate of the battery core products, and the good product rate is to be done well. There are two preconditions: first, high degree of automation of production equipment, and second, engineers using equipment to manufacture Have a deep understanding.

The automation level of the power battery becomes the key to improving the yield
At present, China’s leading power battery manufacturers, represented by CATL and BYD, are not inferior to Panasonic, LG Chemicals, and Samsung SDI in terms of automation of production equipment. However, we must clearly understand that the advantages of Japan and South Korea are not only in their production. On line equipment, more importantly, they have long explored a set of experience in battery quality control. In particular, in the field of ternary batteries, Japanese and Korean companies have a much longer search time than China, and Panasonic and Samsung SDI mass-produced 18650 three-element lithium batteries in terms of voltage, capacity, internal resistance, discharge platform, and constant current ratio. The consistency of key battery indicators has exceeded 90%, and they can be grouped without the need for separate allocation. Domestic production companies rarely do this.
After the double strict consistency check of the battery plant and the car purchase, the products that can not be used for electric vehicles can be called B products. Although China's market is large enough, B-products can be applied in other market segments. However, in the long run, if the A product rate cannot be upgraded, then the A product is to share the cost of the B product. Calculating the cost in this way will have an essential gap with Japanese and Korean companies.
Objectively speaking, at present, China's battery companies are still more aware of the improvement in their efforts to seek quality. Just as Fiona Li Qinghai said: "In terms of battery manufacturing, we should learn Foxconn, and when we do manufacturing, we can do it steadily. Well, do a good job of quality."
In addition to improving the yield rate, expanding the scale is an effective means of reducing costs. CATL's prospectus stated that the cost of its battery system could already reach ninety-six per kilowatt. This shows the cost reduction brought about by the scale effect.
In fact, the growth in the installed capacity in 2017 has slowed down. If the growth rate in 2018 is still relatively low, the increase in cakes in the entire market is limited, and competition is bound to become increasingly severe. In addition, the central government has repeatedly stressed the need to remove local protectionism and shuffle the battery industry. Already coming. Those companies that are lagging behind in technology and whose cost will not run out of price will be eliminated first. This will facilitate the further concentration of high-quality production capacity, form a large-scale comparative advantage, and also contribute to further cost reduction.
The Ideal RJ45 Cat6 Modular Plugs (25-Pack) support speeds associated with Category 6-cable. These plugs offer gold contacts and are suitable for solid or stranded 22 - 23 AWG conductors. Refer to the instructions sheet for terminating the plugs.
- Designed for use with Cat6 universal twisted pair wire
- 50-micron gold contacts
- Suitable for solid or stranded 22 - 23 AWG conductors
- 3-piece, 8-position/8-contact design provides easy installation and optimal performance
- Crimps with a standard RJ-45 crimp die
CAT6 Modular Plug, modular cat 6, 8P8C STP Modular Plug, RJ45 Modular Plug
NINGBO UONICORE ELECTRONICS CO., LTD , https://www.uniconmelectronics.com
