Introduction: Thermistor , as its name implies, is a temperature-sensitive resistor. Its resistance value will change with the change of temperature. What changes will happen in the end? Let's discuss the work of the thermistor with Xiaobian. The principle!
1. Thermistor working principle - introduction
A thermistor is a type of sensitive component. The resistance value of a thermistor changes with temperature. Unlike a general fixed resistor, it is a class of variable resistors and is widely used in various electronic components. Unlike resistive thermometers which use pure metals, the materials used in thermistors are usually ceramics or polymers. The positive temperature coefficient thermistor has a higher resistance value at higher temperatures, and the lower the resistance value of the negative temperature coefficient thermistor at higher temperatures, they belong to the semiconductor device. Thermistors typically achieve high accuracy over a limited temperature range, typically -90°C to 130°C.

2. Thermistor working principle - basic characteristics
Thermistors are sensitive components that are developed early, have many types, and are relatively mature. The thermistors are composed of semiconductor ceramic materials. The thermistors are made of semiconductor materials, mostly with a negative temperature coefficient, that is, the resistance decreases with increasing temperature. Temperature changes cause large resistance changes, so it is the most sensitive temperature sensor.
The main features of the thermistor are:
1) The sensitivity is higher, and the temperature coefficient of resistance is 10 to 100 times larger than that of metal, and the temperature change of 10-6 ° C can be detected;
2) Wide operating temperature range, room temperature device is suitable for -55 ° C ~ 315 ° C, high temperature device is suitable for temperature higher than 315 ° C, low temperature device is suitable for -273 ° C ~ 55 ° C;
3) Small in size, capable of measuring the temperature of voids, cavities and blood vessels in the body that cannot be measured by other thermometers;
4) Easy to use, the resistance value can be arbitrarily selected between 0.1 and 100kΩ;
5) Easy to process into complex shapes for mass production;
6) Good stability and strong overload capability.
3. Thermistor works
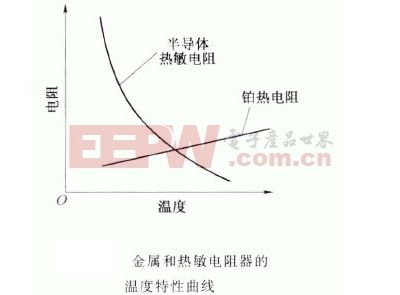
The thermistor is a kind of sensor resistance. The resistance value of the thermistor changes with the change of temperature, which is different from the general fixed resistance. The resistance value of the metal increases with the increase of the planting degree, but the semiconductor is reversed, and its resistance value decreases sharply with the increase of temperature, and exhibits nonlinearity, as shown in the following figure.
As can be seen from the figure, when the temperature changes are the same, the resistance change of the thermistor is about 10 times that of the lead thermal resistance. Therefore, it can be said that the thermistor is particularly sensitive to changes in temperature. This temperature characteristic of a semiconductor is because the conduction mode of the semiconductor is that carriers (electrons, holes) are electrically conductive. Since the number of carriers in a semiconductor is much smaller than that of free electrons in a metal, its resistivity is large. As the temperature increases, the number of carriers participating in the conduction increases in the semiconductor, so the conductivity of the semiconductor increases and the resistivity thereof decreases.
The thermistor is a heat-sensitive element made by utilizing the characteristic that the resistance value of the semiconductor changes significantly with temperature. It is made from certain metal oxides in different formulations. In a certain temperature range, the temperature change of the measured medium can be known by measuring the change of the thermistor resistance.
When the thermistor is installed in a circuit, when the thermistor has the same ambient temperature, the operating time is sharply shortened as the current increases; the thermistor has a shorter operating time and a smaller time when the ambient temperature is relatively high. Maintain current and operating current. When the circuit works normally, the thermistor temperature is close to room temperature and the resistance is very small. The series connection in the circuit does not hinder the current from passing through; and when the circuit has an overcurrent due to the fault, the thermistor increases the temperature due to the increase of the heating power. When the temperature exceeds the switching temperature, the resistance will increase dramatically and the current in the loop will quickly decrease to a safe value.

The working principle of the thermistor is finished, and then we will provide you with several thermistors.
Capacitor For Electric Furnace
Capacitor for Electric Furnace, commonly referred to as capacitors, are capacitors, expressed in the letter C.Definition 1: a capacitor, as the name implies, is a "charging vessel", a device that holds charge.Capacitor.Capacitors are one of the most widely used electronic components in electronic equipment. They are widely used in the fields of interleaving, coupling, bypass, filtering, tuning circuit, energy conversion and control.Definition 2: a capacitor consisting of any two conductors (including wires) that are insulated from each other and are very close together.
Electronic Components Capacitors,High Voltage Capacitors,Low Frequency Capacitor,Water Pump Capacitor,Capacitor for Electric Furnace
YANGZHOU POSITIONING TECH CO., LTD. , https://www.cndingweitech.com
