The history of robots is not long. In 1959, the United States Engelberg and Devol made the world's first industrial robot , and the history of robots really began. Ingeberg studied servo theory at the university, a theory that studies how motion organizations can better track control signals. In 1946, Dvor invented a system that "replayed" the movement of the recorded machine. In 1954, Dvor was patented by a programmable manipulator. This robotic arm works according to procedures and can be programmed according to different work needs, so it is versatile and flexible, both Engelberg and Devol In researching robots, the automotive industry is considered to be the most suitable for working with robots because it is work with heavy machines and the production process is relatively fixed. In 1959, Ingeberg and Dvor teamed up to create the first industrial robot.
I. Reviewing the milestones in the development of robots
According to Techworld, the history of robots dates back to the ancient Greek era, and the philosopher Aristotle once talked about automation tools. The modern origin of robots is the Model T assembly line invented by Henry Ford.
In the Webster's Dictionary, the definition of robots is divided into three categories:
First, a machine that looks like a human can perform a variety of complex human actions (such as walking, talking), but it often lacks human emotions.
Second, devices that can automate complex tasks are good at repetitive tasks.
Third, the mechanism is guided by automatic control. It is very tempting to clarify the development history of the robot in a linear way, from the robot arm manufacturing car (Definition 2) to the humanoid robot (Definition 3) that explores the surrounding environment, and finally the machine can solve the problem by itself and in the game that humans are good at. Defeat humans (Definition 1). However, the development of robots is not so simple.
Techworld Techworld recently took stock of milestones in the development of robots over the past 100 years, from industrial robotic arms to the birth of complex artificial intelligence. The concept of humanoid robots comes from science fiction, mainly the work of American writer Asimov.
Asimov proposed the three laws of robots in 1942:
The first law: robots must not harm human individuals, or witness human beings will be in danger and will not care.
The second law: the robot must obey the command given to it by humans, with the exception of the order that conflicts with the first law.
The third law: The robot should protect its survival as much as possible without violating the first law and the second law.
1950: Turing Test
The word Turing test comes from the paper "Computers and Intelligence" written by Alan Turing, a pioneer in computer science and cryptography, in 1950. Turing believes that if a machine can talk to humans and cannot be identified as a machine, then the machine is smart. Although Turing's method has been criticized by many people for being too simple, it still has a huge impact on human thinking about artificial intelligence.
1948: William Grey Walter makes a turtle robot
Walter was regarded as the first scientist to make an electronic robot, and his robot was called machinaspeculatrix. Whenever the power is reduced, the robot, which looks like a turtle, can find its way to the charging station. Walter's creation laid the foundation for the birth of BEAM (Biology, Electronics, Aesthetics, and Mechanics) robots that do not require a microprocessor to provide computing power.
1954: George Devol applies for a patent for a programmable robot arm
Divor, Norman Heroux, and Joe Engleberger designed and built the first programmable robotic arm, which they called Unimate, and in 1960 Sold it to General Motors. The birth of this industrial robot laid the foundation for these repetitive, difficult or dangerous tasks.
1966: Stanford Research Institute develops Shakey
Between 1966 and 1972, the Stanford Research Institute designed the robot sand base, a milestone in the robotics world, because it combines hardware and software to sense the surrounding environment. After being widely concerned by the media, Shaki brought robots into public awareness.
1996: "Deep Blue" robot defeats chess master Garry Kasparov
In May 1997, IBM robot "Deep Blue" defeated world chess champion Kasparov in the official game. In 1996, it had already defeated Kasparov in a private contest.
2000: Honda launches robot ASIMO
Honda has introduced the classic humanoid robot ASIMO, which is designed as a personal assistant to understand voice commands, gestures, and communicate with the surrounding environment.
2004: IBM Smoke Supercomputer Watson
Watson is the successor to the "dark blue" robot, which made headlines in 2008 when it was in the quiz "Jeopardy!" Defeated humanity. This kind of competition requires the robot to have the complex ability to understand natural language. In 2011, Watson defeated human champions Ken Jennings and Brad Rutter.
2016: Google artificial intelligence system Alpha Go beats the chess champion Lee Sedol
In the Go game held on March 15, 2016, Alpha Go, an artificial intelligence system developed by Google subsidiary and British artificial intelligence startup Deep Mind, defeated the world champion Li Shishi. This is an important milestone for the Deep Mind R&D team. It means that in any case, human-created artificial intelligence can learn how to solve problems. And "dark blue" can only be pre-programmed, only for specific situations.
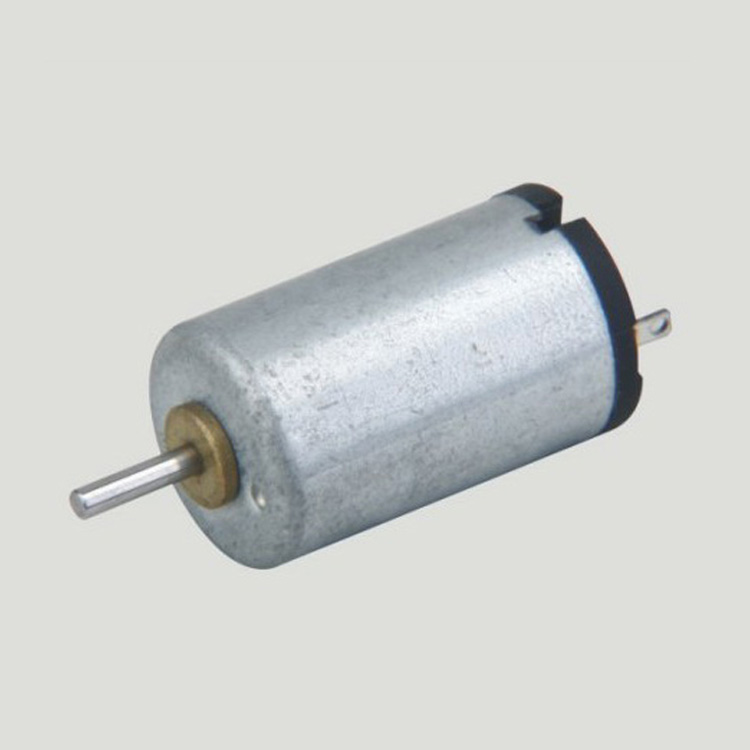
Micro motors Based on Dc Motor, micro motor belongs to the small size of dc motor,micro motor rotor, back cover, chassis, rotor winding is mainly copper, back cover most of the use of plastic material, motor shell use galvanized steel plate, the micro motor can be ROHS test.
A micro motor is any of a class of rotary electrical machines that converts direct current electrical energy into mechanical energy. The most common types rely on the forces produced by magnetic fields. Nearly all types of micro motors have some internal mechanism, either electromechanical or electronic, to periodically change the direction of current flow in part of the motor.



Micro motor is mainly used in: outdoor lamps, electronic toys, model aircraft, intelligent bin, breeze machine, etc



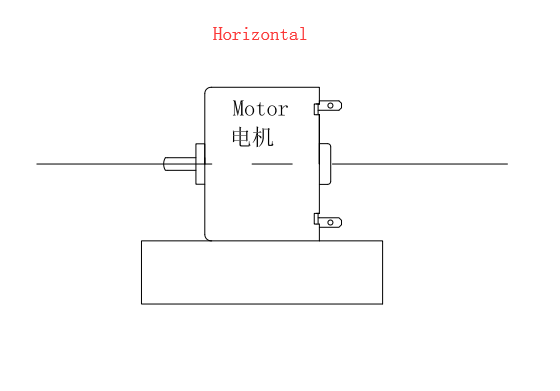
Method of use: the best stable in horizontal plane, installed on the Micro motor output shaft parts, cannot use a hammer to knock, knock prone to press into the micro motor drive, may cause damage to internal components, and cannot be used in the case of blocked.
Operating temperature range:
Micro motor should be used at a temperature of -10~60℃.
The figures stated in the catalog specifications are based on use at ordinary room temperature catalog specifications re based on use at ordinary room temperature (approximately20~25℃.
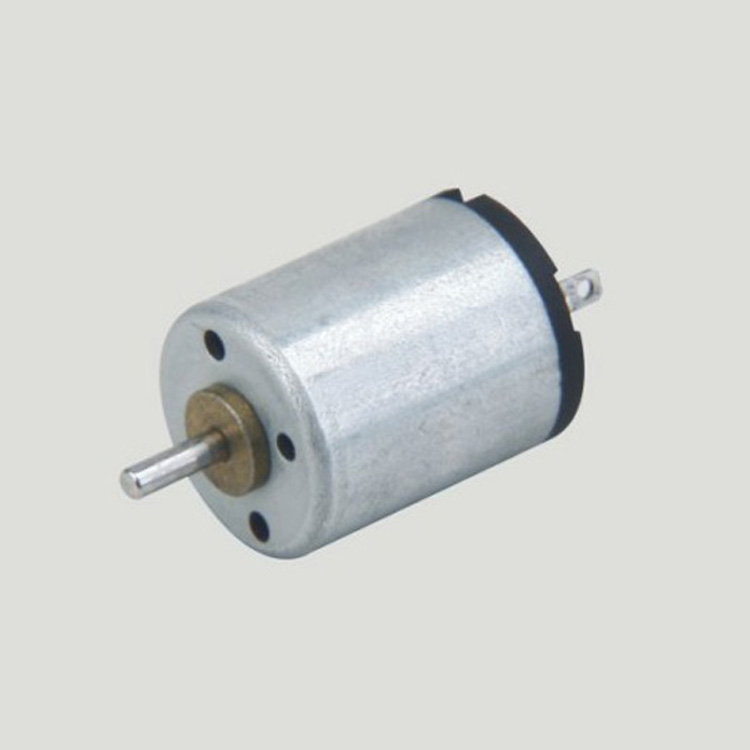


If a micro motor is used outside the prescribed temperature range,the grease on the gearhead area will become unable to function normally and the motor will become unable to start.Depending on the temperature conditions ,it may be possible to deal with them by changing the grease of the motor's parts.Please feel free to consult with us about this.
Storage temperature range:
Micro motor should be stored ta a temperature of -15~65℃.
In case of storage outside this range,the grease on the gearhead area will become unable to function normally and the motor will become unable to start.
Service life:
The longevity of micro motor is greatly affected by the load conditions , the mode of operation,the environment of use ,etc.Therefore,it is necessary to check the conditions under which the product will actually be used .The following conditions will have a negative effect on longevity.Please consult with us should any of them apply.
â—Use with a load that exceeds the rated torque
â—Frequent starting
â—Momentary reversals of turning direction
â—Impact loads
â—Long-term continuous operation
â—Forced turning using the output shaft
â—Use in which the permitted overhang load or the permitted thrust load is exceeded
â—A pulse drive ,e.g.,a short break,counter electromotive force,PWM control
â—Use of a voltage that is nonstandard as regards the rated voltage
â—Use outside the prescribed temperature or relative-humidity range,or in a special environment.
â—Please consult with us about these or any other conditions of use that may apply,so that we can be sure that you select the most appropriate model.
when it come to volume production,we're a major player as well .each month,we rurn out 600000 units,all of which are compliant with the rohs directive.Have any questions or special needed, please contact us, we have the engineer group and best sales department to service to you Looking forward to your inquiry. Welcome to our factory.

Micro Motor,Micro Dc Motor,Micro 3V Motor,Micro Electrical Motor
Shenzhen Shunchang Motor Co., LTD. , https://www.scgearmotor.com
