What is wap business
The WAP service is a basic data service for mobile communications. WAP technology has experienced the development process from 1.x to 2.0. WAP2.0 technology brings new experience to users. Since they are all based on OMA, there are very few differences in WAP implementation under different network technologies. This article will introduce the WAP protocol, the networking, planning, and application of the WAP system, and analyze the differences between the standards, roaming processes, network planning, and applications of different operators. Finally, the development of the WAP service is prospected.
Keywords WAP PULL PUSH OMA WEB2.0 protocol stack gateway
1 WAP business overview
WAP is short for Wireless ApplicaTIon Protocol (wireless application protocol). WAP service is defined as an Internet application service for mobile terminal users. Similar to WWW; mobile users can access WWW content and database information on the Internet using a mobile phone that supports WAP protocol.
The WAP gateway is a key device of the WAP business system; using the WAP gateway, in addition to providing WAP services, it can also provide the bearer of many services such as MMS and positioning, and plays the role of a unified access gateway for data services.
According to the analysis report of the authoritative consulting organization for wireless Internet research, as of the first half of 2007, the number of WAP sites with independent domain names in China had reached 69,000, and the number of mobile Internet users was approximately 45 million. The interactive horizon is a wireless WAP browsing service provided by China Unicom for CDMA; the mobile corresponding service is the mobile Internet service of mobile dream network. In recent years, regardless of whether it is Mobile DreamNet or Unicom's interactive horizon, the growth has been very fast, and business revenue has also shown steady growth. It is the mainstream revenue of data services other than SMS.
2 WAP business standardization process
The standardization of WAP services was initially led by the WAP Forum, and was initially initiated by companies such as Nokia and Motorola in June 1997. The goal of the "WAP Forum" organization is to develop uniform application protocols and usage standards for accessing the Internet in wireless mobile communications. Since its establishment, the organization has successively proposed the framework of WAP standards, WAP1.0 version, WAP1.1 version, WAP 1.3 Version and WAP2.0 version, greatly promote the development of mobile Internet. At present, the "WAP Forum" has been merged into the Open Mobile Architecture IniTIaTIve (OMA), and its work scope has also been extended to all mobile services to create a standard and unified business structure to promote business interoperability.
WAP1.0 standardizes the core content of WAP agreement terms, WML and WMLScript; WAP1.1 supports WBMP format image operation; WAP1.2 version adds PUSH (push), UAPROF (user personal description), and WTA (wireless phone Application) and other technical content, and increased the type of bearer network supported by WAP. Based on previous versions, WAP2.0 adopts a new set of standards and protocols, and proposes an IP signaling protocol.
At home, China Mobile, China Unicom, and China Telecom ’s mobile reserve work have standardized the technical system or requirements for WAP services, mainly based on WAP version 2.0 and the actual situation of their respective networks. The content includes network structure, WAP gateway device requirements, and interfaces Requirements, business processes, authentication, billing and other aspects.
3 WAP business technical principles
3.1 WAP programming model Compared with PC, most wireless devices have weak CPU function, small memory, limited battery power supply, small display screen, and limited input function. WAP is an open and unified platform technology optimized for the characteristics of the wireless environment. It defines a standard set of hardware and software interfaces and provides an application development and operating environment. It follows the WEB methodology and makes the existing internet available. Some development tools can be fully utilized. The WAP programming model is as follows: 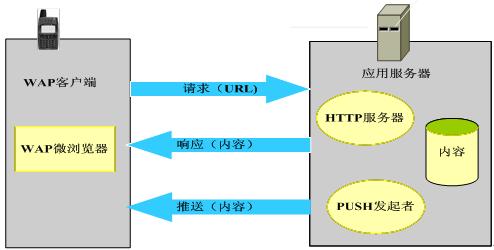
Figure 1 WAP programming model The user end uses a WAP micro browser similar to the IE browser, through which you can access and obtain various information and services expressed in a unified content format. Designers can develop device-independent user interfaces and then use WMLScript (WMLScript) WAP programming language to embed executable logic into mobile terminals. The content on the application server is fully compatible with the WWW content format, and all WWW content can be reused.
3.2 The WAP1.x gateway protocol stack gateway technology is the basis of WAP applications. The basic functions provided by the WAP gateway include: protocol conversion, content encoder / decoder, user agent feature value management, and cache.
The WAP1.x gateway protocol stack adopts a layered design structure, as shown in the following figure: 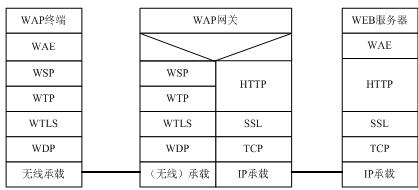
Figure 2 WAP1.x gateway protocol stack
3.3 Compared with WAP2.0 gateway, WAP2.0 protocol stack canceled WSP, WTP, WDP, and replaced it with HTTP and TCP / IP; this improvement of wireless data transmission technology brought the transmission rate and Effectively improve transmission reliability. The general protocol stack of the WAP2.0 gateway is as follows: 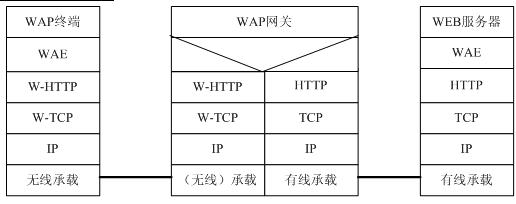
Figure 3 WAP2.0 gateway general protocol stack The WAP gateway in the above figure acts as an HTTP proxy; the WAP gateway can also be used as a business security bearer proxy or direct access transfer point. The protocol stack is as follows: 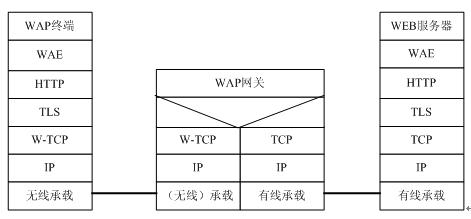
Figure 4 WAP2.0 secure bearer proxy protocol stack
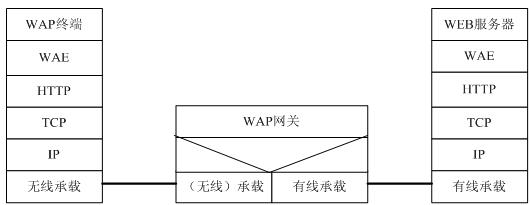
Figure 5 WAP2.0 direct access protocol stack In the solution as a business security bearer proxy, a connection-oriented TLS security tunnel is established between the user terminal and the Web server, providing end-to-end security.
In the direct access scheme, the gateway does not need to use wirelessly optimized TCP and HTTP protocols.
The WAP2.0 gateway includes the following functional modules: WAP PULL proxy, WAP PUSH proxy, WAP support server (including UAProf server that implements terminal capability information management, pre-configuration server TPS that implements automatic pre-configuration of the terminal, wireless phone application WTA server , PKI server for security certification management), etc.
3.4 WAP2.0 business characteristics Through comparative analysis, the main features of WAP2.0 are:
ï® WAP2.0 uses standards such as XHTML and WCSS (WAP Cascading Stylesheets), while maintaining compatibility with WML1.x. Existing tools and resources for developing fixed Internet content and applications can be fully utilized to develop WAP2.0 content and applications; and mobile phones that support WAP2.0 can browse existing www content, greatly enriching application-level content.
ï® Use wireless optimized TCP / IP protocol. At the transport layer, WAP2.0 uses the W-TCP protocol with wireless features, so that the network can perform connection-oriented data transmission based on IP. At the session layer, WAP2.0 uses the W-HTTP protocol with wireless features, and W-HTT is fully compatible with the HTTP / 1.1 protocol.
ï® WAP2.0 provides improved end-to-end security, including the use of TLS protocol and wireless identity module technology (WIM, Wireless IdenTIty Module). The TLS protocol is built on a reliable transport layer, so the adjacent bottom layer must be TCP; unlike WTLS, the serial number is not defined in the TLS frame, and the data packets of the upper layer protocol can be grouped to ensure reliable and safe data transmission. In addition, WAP2.0 uses WIM to provide a more complete and effective end-to-end security mechanism.
In terms of service performance, the enhanced service technologies provided by WAP 2.0 include: data synchronization, multimedia messaging service (MMS), permanent storage interface, provisioning (Provisioning), and pictograms (Pictograms). In addition, WAP2.0 has also strengthened the business functions of wireless telephone application (WTA), Push, and user agent description (UAPROF) based on the previous version.
3.5 WAP2.0 terminal model
WAP2.0 can bring superior business experience to users, and needs the terminal to support the corresponding capabilities. The WAP2.0 terminal model is as follows:

Figure 6 WAP2.0 terminal model where:
ï¬ The application framework provides a WAE execution environment. Under the WAE architecture, content in different manifestations can interact.
ï¬ The network protocol is the handshake procedure between the terminal client and the server.
ï¬ Content management parses different forms of content and presents them to users.
ï¬ General functions provide general functions such as caching and synchronization for various application environments.
ï¬ The WAP Identity Recognition Module (WIM) provides identity identification and encryption algorithms to achieve mutual authentication of the terminal and server.
ï¬ External Functionality Interface (External Functionality Interface, EFI) provides a mechanism for calling external application functions, which can access peripherals such as IC cards, GPS devices, digital cameras, etc., expanding and enhancing the application capabilities of the terminal.
3.6 Standard Differences The WAP service currently carried out by China Mobile can be carried on either the circuit domain of GSM CSD or the GPRS packet network. It can be selected and identified by setting CSD / GPRS and APN: CMWAP on the mobile phone. The use of packet switching has a greater advantage than circuit switching in the utilization of network resources.
The WAP system on China Unicom's CDMA2000 network only provides the bearer of the packet domain, and the service identification is realized by setting the user name and password; corresponding to the WAP service, the user name and password are both WAP. It should also be noted that in the previous WAP 1.2 version of China Unicom's CDMA2000 network, the PUSH service used a special private protocol (UP NOTIFY) and a special private protocol (DOWNLOAD FUN protocol) to support download services. Terminals that support WAP2.0 support HTTP download and no longer support DOWNLOAD FUN, so WAP2.0 terminals cannot use DOWNLOAD FUN download services.
In terms of 3G equipment-related standards, whether in a WCDMA network or a CDMA2000 network, the WAP gateway is in the packet domain, and the protocol standards that are followed fully refer to the relevant OMA specifications, and the HTTP interface is used between the application server and the SMS center. The SMPP interface is based on IP bearer on the mobile network side and uses WSP or W-HTTP protocol to implement services. The WAP gateway devices under the two network structures are almost the same.
4 WAP business service system planning For the WAP gateway, there is no essential difference in running on different networks. The main difference is that the service mode or business process defined by the operator causes the WAP gateway to adjust its external interface.
The planning of the WAP business system mainly considers network organization, network element capacity calculation, network element setting, interconnection and interworking, and bandwidth requirement calculation.
4.1 Network Organization
The network organization of the WAP system is similar to the WEB system of INTERNET, as follows:
Figure 7 Network structure of the WAP system. The WAP gateway is located between the mobile bearer network and the Internet application server and is the core network element of the WAP service system.
In actual operation, WAP business system needs to include AAA / RADIUS server and management, business support system, in order to achieve authentication, authentication and accounting.
In addition, in order to achieve operation and maintenance, statistics, network management, monitoring and other functions, the WAP gateway needs to be connected to the network management platform.
The WAP gateway also needs to provide services for browsing services and data services such as MMS and streaming media. Therefore, the WAP gateway should implement support for DNS and ENUM-DNS protocols and be connected to related business engines. DNS support means that when the WAP terminal performs PULL browsing, it needs to rely on DNS to resolve the URL domain name in the terminal browsing request to the corresponding IP address to correctly route to the corresponding CP / SP. For ENUM-DNS support, it means that the WAP gateway needs to map the information of the service server to which it belongs according to the terminal MSISDN number.
The WAP portal site serves as an interface presented by WAP business users, provides service guidance, and aggregates links of various business sites. Generally, the WAP terminal accesses the portal site first after accessing the network, and enters various service sites or other portal sites through the portal site.
4.2 Calculation of Gateway Capacity Calculation In addition to considering the user's business requirements for mobile Internet, WAP gateway capacity needs to also comprehensively consider the service volume and user distribution of MMS, JAVA downloads, location services and other bearer services. The work involved in the capacity calculation of the WAP gateway includes user prediction, business penetration rate prediction, business model construction, and gateway processing capacity calculation.
4.3 Gateway and portal settings
WAP gateways are generally configured according to processing capabilities, and some are based on the number of users, in fact there is a correspondence between the two. In the early days of network construction, the main sharding settings, and centralized setting of WAP gateways in key areas where mobile data services are developing rapidly. With the continuous expansion of business needs and scale, it is gradually dispersed. The setting of the gateway needs to determine the coverage area, setting capacity, office setting, office points, etc.
The client and server of the WAP2.0 protocol can directly use HTTP / 1.1 communication, so as far as WAP2.0 itself is concerned, it is not necessary to set a WAP gateway, but when providing Push service, the gateway needs to function as a PPG; in addition, for optimization The communication process provides more location-based services and personalized services. It is necessary to configure a WAP gateway.
The selection of WAP gateway should fully consider the needs of business development and ensure the compatibility of the entire system.
The default homepage should be set on the WAP gateway. When the user terminal is not set to access the homepage, the WAP gateway will guide the user to access the default homepage. The gateway IP address should be set on the user's WAP terminal.
In addition, general operators will set up their own WAP service portal sites, which generally use public IP addresses to access the public network.
4.4 Authentication and accounting
WAP authentication includes two levels: packet network access authentication and WAP service authentication. Access authentication is implemented by the WAP gateway assisted by the AAA / RADIUS server; the WAP gateway records the binding relationship between the MSISDN number and IP address of the online terminal; when the terminal goes offline, the WAP gateway clears the binding relationship. The authentication of the WAP service needs to be completed by the WAP gateway in cooperation with the management and support platform; after the WAP user accesses the authentication through the packet network, it is routed to the WAP gateway to which it belongs according to the gateway address set in its mobile phone. Perform identity authentication; business authentication can use two methods: calling number authentication and user name / password authentication.
In terms of charging, the WAP gateway first matches related services, generates a detailed original bill, and transmits it to the corresponding charging center.
4.5 Roaming process design Maintaining a unified user experience is one of the design concepts of the 3G service network. Under this concept, the 3G service must provide attribution to provide services. In Telecom's 3G planning scheme, WAP gateways are set up in different provinces. The WAP service of roaming users is required to be accessed by the home WAP gateway, and the home WAP gateway provides services for users.
In China Unicom's CDMA20001X network, WAP gateways are set up in large areas (a platform management system is set for each gateway system), following the principle of gateway access in the visited area. When a user roams, the roaming agreement of the integrated management and support platform can be used to obtain the customized information of the home user. The routing can be divided into two cases:
1) When there is a large area gateway in the visited area, the WAP terminal is directly connected to the large area gateway after accessing through the visited area PDSN. The WAP management platform connected to the gateway completes the service authentication and obtains the customized information of the user through the roaming agreement In order to visit the corresponding portal site.
2) In the case where the WAP gateway is not set in the visited place, the WAP terminal first accesses through the visited PDSN, and the PDSN converts the internal reserved gateway address set by the WAP terminal into the IP address of the WAP gateway in the region where the visited place belongs, and then establishes the After the gateway is connected, the user can access the customized portal site after passing the authentication.
4.6 Interconnection organization The interconnection organization needs to combine the routing principles and the above results to formulate an interconnection plan between the service network and the access network, core network, support system, and other networks, and clearly define the bearer method and interface protocol to be adopted.
WAP can support various mobile networks, such as GSM, CDMA, PHS, 3G, etc. For different bearer networks, WAP networking can be based on short messages, circuit switched data (CSD) and packet networks.
WAP gateway equipment needs to carry a large amount of business data. Therefore, on a packet-bearing network, a WAP gateway generally accesses an IP network node nearby, and is connected to core network equipment and other service engines through an IP bearer network. To ensure the security of service data, the WAP gateway and other mobile network devices are usually interconnected through VPNs, such as MPLS VPN or IPSec VPN.
The WAP gateway needs to configure an internal address for the gateway addressing of mobile phone access; in order to communicate with the mobile packet network, an additional IP address needs to be set. This address can be private or public IP, and the core network address allocation scheme be consistent. In addition, in the case of independent networking of mobile networks (such as the establishment of VPNs with private addresses), if you want to achieve direct access to the Internet service, you need to configure the public network address; but for security reasons, firewalls are usually configured to achieve security control Features. If users who have reserved IP addresses need to access the WAP portal, they need to use gateways or firewalls as NAT or use tunneling (such as GRE) to re-encapsulate business data packets.
4.7 Calculation of bearer bandwidth On the basis of the network interconnection structure, it is necessary to calculate the bandwidth requirements of each network element interface based on the interface bearer mode, service model, and service volume calculation results. The bandwidth requirements of the WAP gateway interface must not only consider the service bandwidth requirements, but also the system overhead bandwidth requirements. The actual bandwidth configuration should consider setting a certain redundancy on the basis of bandwidth requirements.
4.8 Other problems The general method to access the WAP gateway is to set the IP address of the WAP gateway on the mobile terminal. In the existing network of the operator, this IP address is usually set to the same IP private address throughout the entire network. In the case where roaming and core packet devices are connected to multiple WAP gateways at the same time, the core packet devices are often required to have a routing function to identify the home WAP gateway according to different attributes of users, which is lacking in GGSN / PDN devices on the existing network Next, you can determine the URL (configure the URL of the home WAP gateway on the mobile terminal) and complete the addressing of the WAP gateway through DNS resolution; this can solve the problem relatively easily and achieve load sharing among multiple WAP gateways. .
5 Typical application cases of WAP business
The WAP service provides users with a mobile Internet experience, including WAP browsing, download services, and various services based on WAP Push. In addition, WAP also provides some other services, such as MMS, JAVA downloads, mobile location business service content delivery, and provides data transmission services and Push notification functions for the realization of other services, which is the basis for developing mobile data services. .
The following lists some typical WAP services and applications of the two major domestic operators (China Mobile and China Unicom).
The mobile Internet service of China Mobile Mobile Dream Network provides the following services:
Table 1 Mobile dream network mobile Internet service 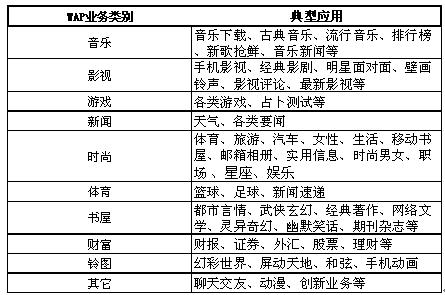
The interactive world of China Unicom provides the following services:
Table 2 Services provided by Interactive World
The above services cover all aspects of entertainment, business and life, and provide users with a means to enjoy endless online information or online resources, which fully reflects the value of mobile Internet.
6 The outlook for WAP business development is similar to broadband Internet. E-commerce, online banking, and mobile mail systems are some of the concerns for the next step of WAP business development. Last year, Guangdong Mobile launched the "Mobile Wallet" service with the Guangdong Branch of China Construction Bank and China Merchants Bank. Customers only need to bind their mobile phone number to their bank account to use their mobile phones to make self-assistance at any time within 24 hours. Using WAP's push technology to realize mobile e-mail function, compared with the e-mail system in the Internet, the timeliness is greatly improved, and the amount of information is greatly improved compared to the e-mail function provided by the short message system.
From the development of the Internet, we can also see the huge potential and bright prospects of WAP business development. Web2.0 emphasizes the ideas and concepts of information exchange and sharing. It uses six-degree separation theory and technologies such as xml and ajax (asynchronous JavaScript and XML). The main application forms include blog (BLOG), site summary (RSS), and encyclopedia Encyclopedia (Wiki), web abstract (TAG), social network (SNS), P2P, instant messaging (IM), etc. Web2.0 has brought about a major change in Internet applications: people will be the producers, communicators and demanders of content delivered over the Internet. The cohesiveness of WAP2.0 and Web2.0 expands the connotation of Web 2.0 to the client, and makes the content "moving" up, bringing tremendous flexibility and scalability. Undoubtedly, the combination of the two will greatly promote the market of mobile phone betting, mobile phone reading, mobile phone media and so on.
Even in the 3G era, the limitations of mobile phone terminals and air interface resources still exist, and device and system resources in the wireless environment still need to be optimized, so WAP applications are still indispensable.
3000A Fuse for the Protection,The Protection of Semiconductor Device,Fuse for the Protection
YANGZHOU POSITIONING TECH CO., LTD. , https://www.yzpst.com
