The integration of the three networks refers to the development and evolution of the telecommunication network, the broadcasting and television network, and the Internet in the next generation telecommunication network, the next generation broadcasting network, and the next generation Internet. The functions of the network tend to be consistent and the service scope tends to be the same. All can provide users with a variety of services such as making calls, surfing the Internet and watching TV.
The essence of triple play is that the future telecom network, the wide-area network and the Internet can carry multiple information services and create more kinds of converged services instead of three networks to synthesize one network. Therefore, the triple play is not triple play. one. The possible development direction of the triple play is as shown in the following figure, from technology convergence, service convergence, industry integration to final terminal convergence and network convergence.
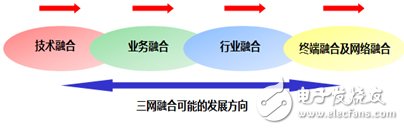
Figure 1 Possible development direction of triple play
IPTV/CATV is the starting and key of triple play
The key to triple play is the convergence of telecommunications and broadcasting services. Telecom operators and broadcasting and TV operators will penetrate each other and become full-service operators, competing for customers through full-service binding and price strategy. Telecom operators will provide IPTV services by laying ultra-bandwidth metropolitan area networks and robbing cable TV. Operator TV business, cable operators may enter the mobile field of traditional telecom operators by self-built or MVNO, and the whole business competition will be faced. The two sides are facing unprecedented competitive pressure, based on full-service competition, and IPTV/CATV It is the starting point and key to the triple play.
At present, the network bears IPTV and faces many difficulties: First, the current network does not meet the end-to-end speedup: HD needs 10~20M, and the current home bandwidth is generally lower than 4M. To achieve end-to-end speed, some access devices BRAS and core routers need to be modified. Secondly, the service experience is difficult to guarantee: most of the traffic of the broadband IP metropolitan area network is Internet service. The planning, design and construction of the existing network basically do not consider the bearer of the IPTV service, and the switching ratio of the IPTV channel is The traditional TV experience is poor, and it is very sensitive to packet loss, which seriously affects the user experience. Third, the lack of end-to-end management means: the operation and maintenance of the bearer network involves the IPTV service system, the bearer network and the set-top box, and the operation and maintenance department involves multiple fields. In many departments, it is difficult to quickly demarcate and quickly locate. Finally, more network layers will become the bottleneck of quality. At present, the metropolitan area network is generally 5 hops, and the IPTV-related bearer technology is difficult to be uniformly deployed. Carrying IPTV, network construction costs, network service control, network service quality, etc. will bring more problems, so the three networks Convergence puts new demands on the access network.
Access network flat development
The first is the convergence and unification of access networks. The separated networks are transformed into multi-service integrated access. The PON network provides the possibility for unified access of small and medium-sized enterprises, building micro base stations and residential users, while the integration of services and the unification of equipment further Promote the convergence of FTTX networks, reduce network nodes, simplify network hierarchy, and reduce network TCO costs. Second, for operator-wide full-service management, the maintenance of current networks is managed by different vertical business units, and in the triple-play environment. Under the unified OLT must face the management of different departments to achieve virtualization of management. Finally, to differentiate the end users, OLT devices must face two-dimensional networks, that is, different services + different customer groups, provide different QoS guarantees, and truly realize customer differentiation.
In the face of the broadcasting and TV operators under the triple play, the access network needs to develop toward a flattening trend. As shown in the following figure, the point-to-point transformation architecture of the optical copper withdrawal network is a five-level architecture with many network nodes. The new technology combination architecture of the copper retreat is a three-level architecture, and the number of nodes is reduced by 80%. The large capacity and the small office are the consensus in the industry. With the improvement of PON technology, greater bandwidth, greater split ratio, and farther communication Distance has become a trend in access technology development.
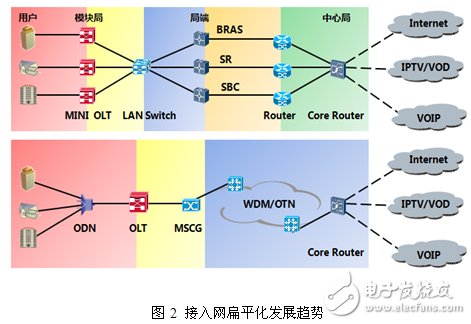
Transmission network flat development
The development trend of the flattening of the access network has also brought about some changes in the transmission network. First, the consumption of optical fiber resources has become large. The OLT/DSLAM directly connected to the BRAS/SR requires a large amount of optical fibers, which may result in insufficient optical fiber resources in some areas. Home services (including voice and video services) require high security network protection; BRAS needs higher security backup. In the future, BRAS hot backup, OLT uplink needs to consume more fiber, which is required for working and protecting fiber. In the case of different cables, BRAS/OLT has the demand for long-distance lasers. On the other hand, for large customer lines, optical fibers need to be directly connected to SR, so that the fiber utilization rate is not high, and there is no protection. The security cannot meet the requirements of large customers. . Therefore, the transmission network needs to be developed to flatten, as shown in the following figure:
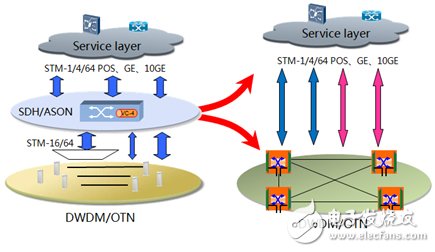
Figure 3 The development trend of the flattening of the transmission network
Alarm release mainly uses standard equipment such as audio alarms. During wartime, communication, broadcasting, and television systems must prioritize the transmission and issuance of air defense alarm signals, and auxiliary means such as sirens, horns, and gongs can also be used. The sound alarm must be set at the designated location, and the alarm facilities must be maintained in good working condition. The release and transmission of alarms should be fast and accurate, and multiple means should be used simultaneously; Strengthen communication and liaison with superiors, subordinates, and neighbors, receive air raid intelligence information at any time, strengthen observation of air targets, and promptly report air raid intelligence; According to the situation and duration of the air raid, timely release the warning signal. With the sudden increase of air raids, the increase of attack methods, and the expansion of destruction, the importance of air defense alerts is increasingly being valued. The accuracy, timeliness, and continuous issuance ability of air defense alerts are required to be higher. The issuance methods of air defense alerts will also become more flexible and diverse with the construction and improvement of communication and network.
Early Warning System, Control Devices, Electronic Sirens, Natural Disaster Warning System, Alarm System
Taixing Minsheng Electronic Co.,Ltd. , https://www.msloudspeaker.com
